In previous blogs, you have learned how our respiratory system works and how we breathe. Our lungs have a vital role in breathing in and breathing out. This time, we are going to take a look at how gas exchange occurs within the lungs.
Gas Exchange
- is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the lungs and bloodstream.
- Gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone which includes the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli.
Recap: The main function of the respiratory system is to consistently supply oxygen to the tissues and to remove carbon dioxide so it does not accumulate.
Gas exchange occurs between the alveoli and the capillaries that surround them. Deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart enters the lungs via the pulmonary artery and then enters into tiny capillaries within the lungs. The blood in the capillaries will then release carbon dioxide into the lungs to be exhaled and pick up oxygen that has been inhaled. This oxygenated blood then goes back to the left side of the heart to be pumped throughout the body delivering oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to all the tissues.
Diffusion – is the movement of substances from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Note: Air is a mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, water, vapor and carbon dioxide.
- The partial pressure of a specific gas is determined by multiplying atmospheric pressure by the percentage of the specific gas in atmospheric gas.
- The partial pressure of a gas depends on:
- Concentration – the greater the concentration of the gas the greater its partial pressure will be.
- Solubility – the more soluble a gas is in a fluid, the less it wants to “escape”.
Example: carbon dioxide is much more soluble in water (blood) than oxygen.
- External Gas Exchange
- Transfer of oxygen from alveoli to blood.
- Transfer of CO2 from blood to alveoli.
- Gas Diffusion across pulmonary membrane depends on two main factors:
- Partial pressure gradients between alveolar air in the blood.
- Health of lung issue.
Note: Majority of oxygen carried in the blood is bound to hemoglobin which is found in the red blood cells.
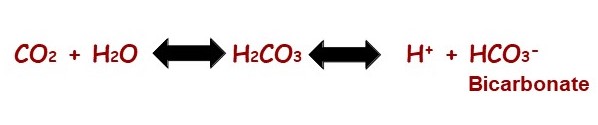
Carbon dioxide is soluble 80%-90% is carried in the blood as bicarbonate.
Recap:
- Partial pressure of oxygen, greater in alveoli
- Therefore, oxygen can diffuse easily from alveoli to blood.
- Partial pressure of carbon dioxide, greater in the capillaries
- Therefore, CO2 can easily diffuse from the capillaries to the alveoli.
What are some things that can affect gas exchange?
- Membrane thickness – thinner membrane
- Membrane surface – less surface area
- Pressure differences across the membrane
To see this explained in video format, check out my video on “How does Gas Exchange Occur in the Lungs?“